What Is The Most Likely Explanation For The Smaller Size Of The Hypoxic Zone In The Year 2000?
2021 Gulf of Mexico Hypoxic Zone Size
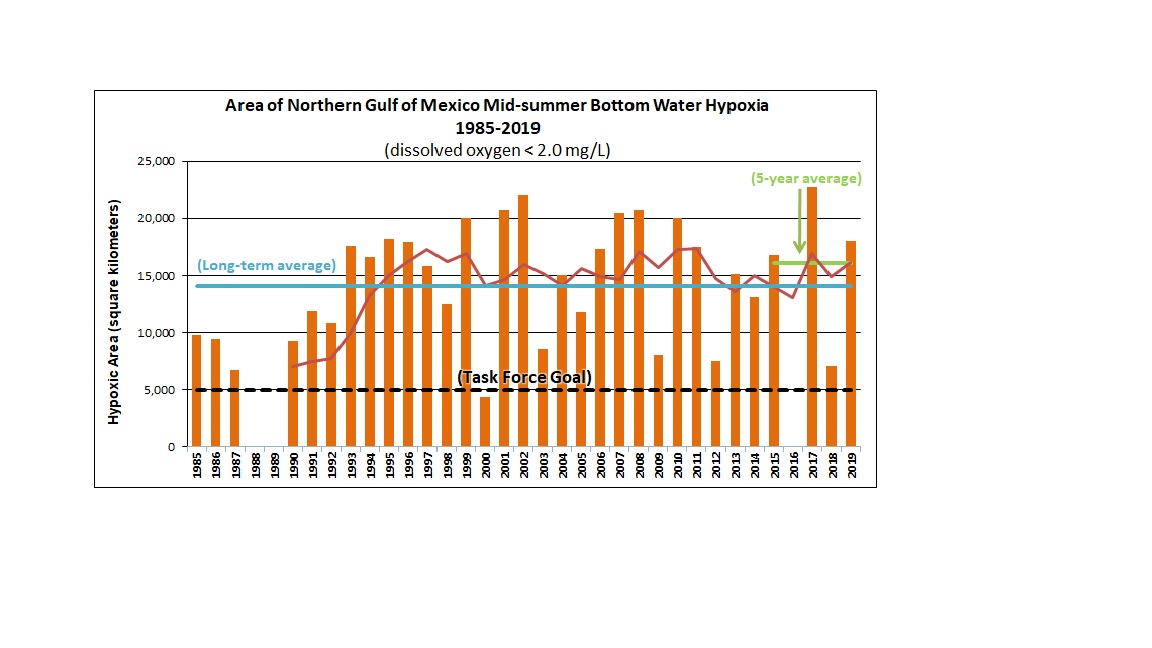
NOAA-supported scientists appear that the 2021 Gulf of Mexico "dead zone" is approximately 6,334 square miles, or equivalent to more than than four million acres of habitat potentially unavailable to fish and lesser species.
The boilerplate hypoxic zone over the by five years is 5,380 foursquare miles. Since records began in 1985, the largest hypoxic zone measured was 8,776 square miles in 2017.
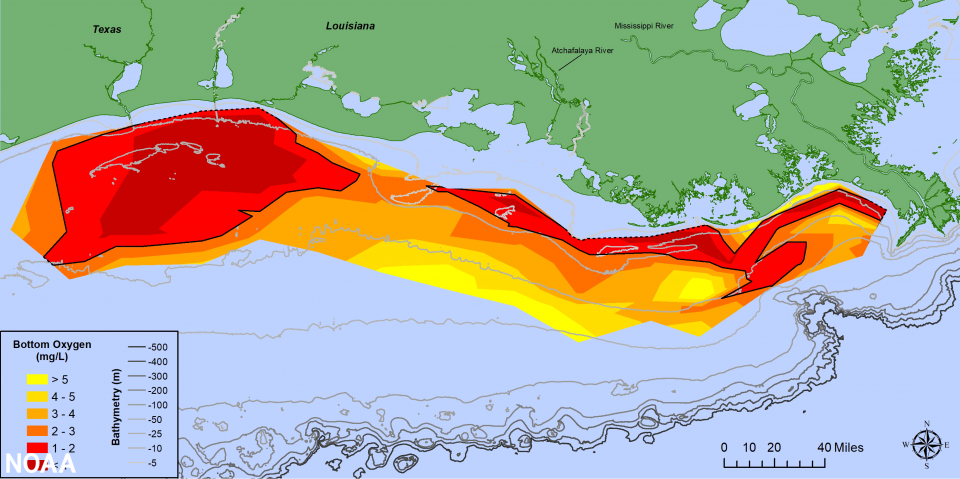
2021 Forecast: Summertime Hypoxic Zone Size, Northern Gulf of Mexico
NOAA and the Us Geological Survey (USGS) released their summer hypoxia zone size in the Northern Gulf of Mexico on June iii, 2021. Read the full press release here. Scientists are forecasting this summer's Gulf of Mexico hypoxic area or "dead zone" – an expanse of low to no oxygen that tin impale fish and other marine life – to be approximately 4,880 square miles, larger than the long-term average measured size of v,400 foursquare miles but substantially less than the tape of 8,776 square miles in 2017. The annual prediction is based on a suite of models that incorporate USGS river-flow and nutrient data.
2020 Gulf of United mexican states Hypoxic Zone Size
The 2020 Gulf of Mexico hypoxic zone or "dead zone" measured 2,116 foursquare miles and was the 3rd smallest in the 34-year tape of surveys. The 5-year average is at present down to v,408 square miles. The earlier forecast for the dead zone was higher at vi,700 foursquare miles. A major factor for the smaller measured size was due to all-encompassing mixing caused past hurricane Hanna, which passed through the Gulf right ahead of the survey cruise. For more than information, see the Lousiana Universities Marine Consortium (LUMCON) and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) press releases.
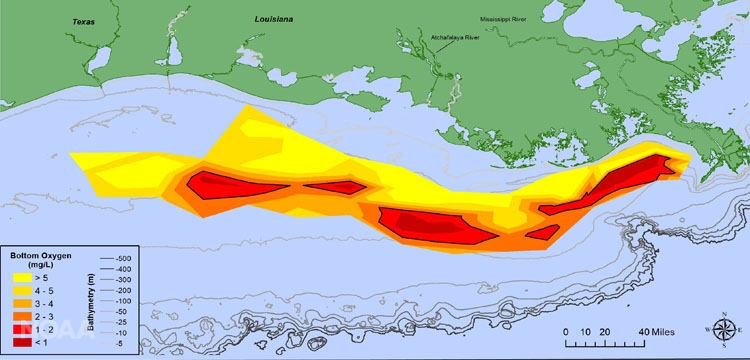
2020 Forecast: Summer Hypoxic Zone Size, Northern Gulf of Mexico
NOAA and the United States Geological Survey (USGS) released their summertime hypoxia zone size in the Northern Gulf of United mexican states on June iii, 2020. Read the full press release here. Scientists are forecasting this summer'due south Gulf of Mexico hypoxic area or "expressionless zone" – an area of low to no oxygen that can kill fish and other marine life – to be approximately 6,700 square miles, larger than the long-term boilerplate measured size of 5,387 square miles but substantially less than the record of eight,776 foursquare miles set in 2017. The almanac prediction is based on U.S. Geological Survey river-menstruum and nutrient information.
2019 Gulf of Mexico Hypoxic Zone Size

The 2019 Gulf of Mexico hypoxic zone or "dead zone" measured 18,005 square kilometers (six,952 square miles), the eighth largest area mapped since 1985. It is slightly smaller than the 20,277 square kilometers forecasted by NOAA in June 2019 and larger than the Hypoxia Task Force Goal of 5,000 square kilometers. Researchers constitute that Hurricane Barry's inflow prior to measuring the zone helped mix the water cavalcade, merely it only temporarily disrupted the already formed hypoxic zone. For more data, meet the Louisiana Universities Marine Consortium (LUMCON)and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) printing releases.
2019 Forecast: Summer Hypoxic Zone Size, Northern Gulf of Mexico
NOAA and the United States Geological Survey (USGS) released their 2019 forecast for the summer hypoxic zone size in the Northern Gulf of United mexican states on June 10, 2019. Read the full press release. Scientists are expecting the 2019 area of low oxygen, commonly known as the 'Dead Zone,' to exist approximately 7,829 square miles, or about the size of Massachusetts. This prediction is large primarily because of loftier spring rainfall and river belch into Gulf.
2018 Gulf of Mexico Hypoxic Zone Size

The 2018 Gulf of Mexico hypoxic zone or "dead zone" measured 7,040 square kilometers (ii,720 square miles), the 4th smallest area mapped since 1985. Information technology is considerably smaller than the 14,970 foursquare kilometers forecasted by NOAA in June 2018, nonetheless nevertheless larger than the Hypoxia Job Strength Goal of 5,000 square kilometers. Researchers suggest that persistently strong westerly winds and waves likely led to enhanced mixing conditions and smaller-than-expected zone size. For more information, run into the Louisiana Universities Marine Consortium (LUMCON)and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Assistants (NOAA) press releases.
2017 Gulf of United mexican states Hypoxic Zone Size

The 2017 "Dead Zone" measured 22,720 square kilometers (8,776 foursquare miles). This size is close to the forecast made in June. Researchers suggest that the Mississippi River May discharge, which was well above average, provides an explanation for most of the large zone measurement. For more information, read the Louisiana Universities Marine Consortium (LUMCON) and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)press releases.
2016 Cruise to Mensurate Gulf of United mexican states Hypoxic Zone Size Cancelled
Due to mechanical problems with the NOAA transport designated for the measurement cruise, the hypoxic zone was non measured in 2016. Read the full press release for more information.
2015 Gulf of Mexico Hypoxic Zone Size
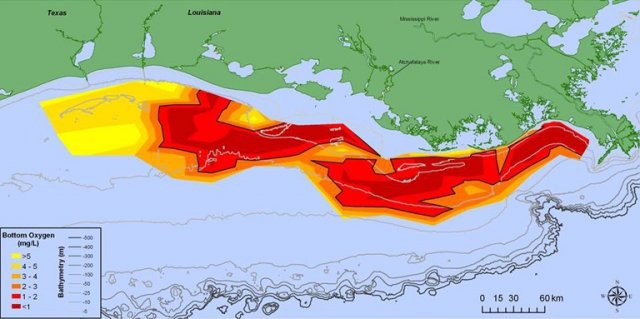
The 2015 "Dead Zone" measured sixteen,760 square kilometers (6,474 foursquare miles). This size is larger than the predicted range made in June. Researchers advise that heavy rains in June and loftier river discharges in July may provide an explanation for the larger zone measurement. Read the Louisiana Universities Marine Consortium (LUMCON) and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)printing releases.
2014 Gulf of Mexico Hypoxic Zone Size
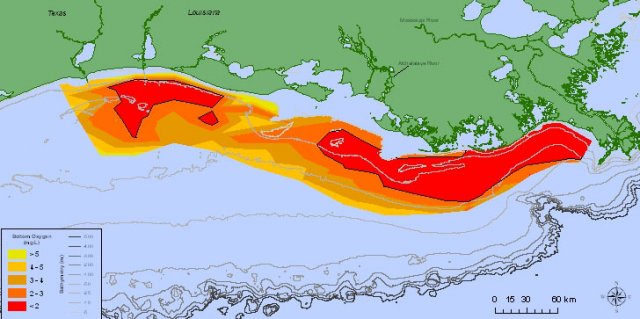
The 2014 "Dead Zone" measured thirteen,080 square kilometers (5,052 square miles) as of August 1, 2014. This size cruel inside the predicted range made in June. Read the LUMCON press release and the NOAA press release.
Measuring the Hypoxic Zone
The hypoxic zone in the northern Gulf of Mexico is an expanse along the Louisiana-Texas coast, where h2o nearly the bottom of the Gulf contains less than two parts per million of dissolved oxygen, causing a condition referred to every bit hypoxia.
Each summer, the size of the hypoxic zone is measured. The size of the zone is an important indicator of how much progress is being fabricated to reduce nutrient inputs into the Gulf of Mexico. Sometimes the size of the zone is influenced by other factors, such as droughts or hurricanes that can reduce the size of the zone, or floods that can increase the size.
Information about the size of the hypoxic zone can be obtained from NOAA'due south Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Spotter and the LUMCON, which is supported by NOAA's NGOMEX.
The Gulf of United mexican states Hypoxia Watch evolved as a cooperative project among NOAA's National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS), the National Coastal Information Development Centre (NCDDC), and the CoastWatch - Caribbean/Gulf of Mexico - Regional Node. The objective of Hypoxia Watch is to develop new near-real time data and map products using shipboard measurements of bottom-dissolved oxygen and disseminate them over the Internet. Access measurements taken from 2001 to the current season.
What Is The Most Likely Explanation For The Smaller Size Of The Hypoxic Zone In The Year 2000?,
Source: https://www.epa.gov/ms-htf/northern-gulf-mexico-hypoxic-zone
Posted by: pondercosertrut1966.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is The Most Likely Explanation For The Smaller Size Of The Hypoxic Zone In The Year 2000?"
Post a Comment